About Psoriasis, things you should know

about Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a
complex autoimmune disease that profoundly impacts not just the skin and joints
but also the psychological well-being of individuals. People suffering from
psoriasis frequently grapple with anxiety and a diminished sense of self-worth
due to the visible nature of the condition, which often leads to social stigma
and self-consciousness. Despite the availability of multiple treatment options,
managing psoriasis proves to be challenging due to its persistent and chronic
nature.
Psoriasis manifests in various forms, affecting
approximately 2-3% of Western populations equally across both sexes and at all
ages. It frequently presents as plaques on the knees
and elbows but can affect any part of the skin, including more sensitive areas
like the scalp and genital region. The underlying cause of psoriasis is rooted
in the immune system, involving a type of white blood cell known as a T cell.
In individuals with psoriasis, these T cells are mistakenly activated,
triggering an overactive immune response that results in inflammation and an
accelerated turnover of skin cells.
About PSORIASIS, who is affected
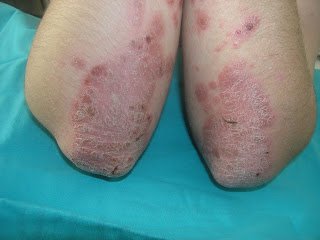 Ellbows affected with psoriasis
Ellbows affected with psoriasisThe treatment of
psoriasis is no straightforward task due to the tendency for affected skin to
grow resistant to therapies over time, particularly with repeated use of
topical corticosteroids. This resistance requires physicians to adopt a
trial-and-error approach in managing the condition, often having to switch
treatments every 12 to 24 months. This strategy helps to mitigate the
possibility of adverse reactions and offers a chance to find a more effective
solution.
The management of
psoriasis by expert dermatologists is typically staged, with treatments being
tailored based on specific factors such as the severity of the condition, the
size of the affected areas, the type of psoriasis diagnosed, and how the
patient responds to initial treatments. In the initial stage, topical
treatments are commonly employed. These medications are applied directly to the
skin and can help control mild to moderate psoriasis by reducing inflammation
and slowing down the rapid turnover of skin cells.
You have permission to reprint this article as long as no changes are made and the complete resource box is included."
Treatment strategies
for psoriasis are diversified and extend beyond topical applications. For more
severe cases, phototherapy and systemic treatments may be considered.
Phototherapy involves using natural or artificial ultraviolet light to reduce
symptoms, while systemic treatments involve oral or injected medications that
work throughout the body to address psoriasis internally. These treatments are
often necessary when psoriasis covers a substantial portion of the body or
particularly sensitive areas, or when the condition has a significant impact on
the patient's quality of life.
Despite the multitude
of treatments available, the chronic nature of psoriasis makes long-term
management a daunting process. The efficacy of
treatments can dwindle over time, underscoring the importance of regular
monitoring and adjustment by healthcare professionals. Patients often find themselves on a continuous journey
of treatment modification, learning to manage expectations and stay informed
about the latest treatment advances.
Aside from medical
treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing
psoriasis symptoms. Stress reduction, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding
smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and regular moisturizing to prevent
dry skin are all essential strategies that can help manage flare-ups. Support
groups and counseling might also assist individuals in coping with the
emotional and psychological impacts of the disease, further improving their
quality of life. about psoriasis
There are numerous TREATMENTS
Raising awareness
about psoriasis and tackling the stigma associated with it is vital for
fostering an understanding and supportive environment for those living with the
condition. Education on the nature of psoriasis as a non-contagious autoimmune
disease can help correct misconceptions and lead to greater empathy and support
from the public.
Expert dermatologists typically treat psoriasis in stages based on the severity of the condition, the size of the affected areas, the type of psoriasis, and the patient's response to initial treatments. In the first stage, medications are applied to the skin (topical treatment)."
Ultimately, the journey
towards managing psoriasis is a continuous one, requiring collaboration between
patients and healthcare providers to develop a personalized and adaptive
treatment plan that aligns with individual needs and lifestyles. Constant communication,
regular check-ups, and a proactive approach in exploring new treatment
methodologies are crucial components in the effort to control the disease
effectively.
In conclusion,
while psoriasis remains a challenging condition to manage due to its chronic
nature and the potential for treatment resistance, comprehensive care and a
holistic approach encompassing both medical and lifestyle strategies offer the
best chances for patients to lead fulfilling lives. With ongoing research and
awareness initiatives, there is hope for even more effective and targeted
treatments in the future, enhancing the quality of life for those affected by
this persistent disease.
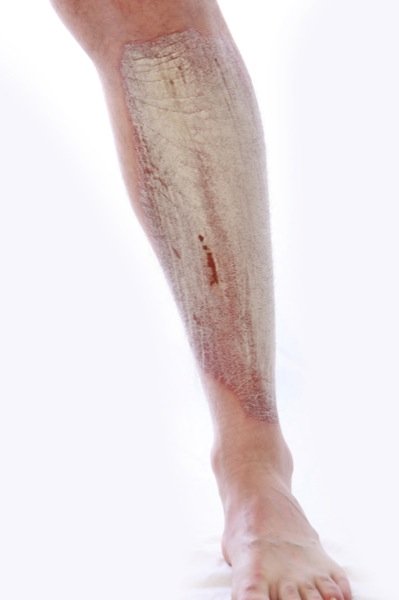 Psoriasis on the leg
Psoriasis on the legPágina de inicio
Mapa del sitio
Mapa del sitio en orden alfabético